The Confederacy lives on in several official US state flags
According to Whose Heritage?, a report by the Southern Poverty Law Center on public symbols of the Confederacy, progress over the past two years on removing statues, flags, and other symbols from public places has been slow.
The 2015 massacre of nine African Americans at the historic “Mother Emanuel” church in Charleston sparked a nationwide movement to remove Confederate monuments, flags and other symbols from the public square, and to rename schools, parks, roads and other public works that pay homage to the Confederacy. Yet, today, the vast majority of these emblems remain in place.
In this updated edition of the 2016 report Whose Heritage?, the SPLC identifies 110 Confederate symbols that have been removed since the Charleston attack — and 1,728 that still stand.
Still very much standing, for instance, the Mount Rushmore of the Confederacy in Georgia, a massive stone carving featuring Jefferson Davis, Robert E. Lee and Thomas “Stonewall” Jackson.
And perhaps even worse, not represented on this map are Confederate symbols that are part of the official identities of many Southern states. Did you know Mississippi’s official state flag still contains the Confederate battle flag?
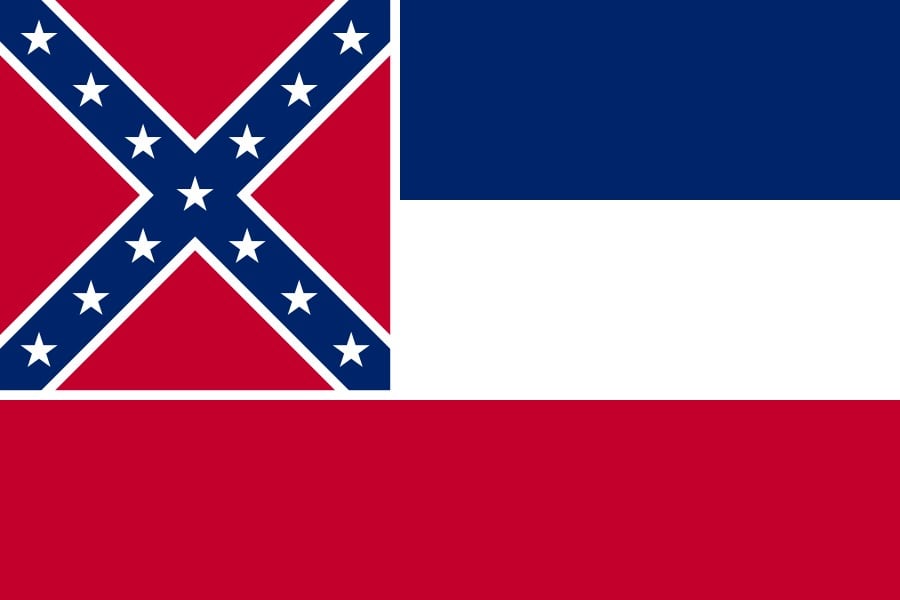

As of the 2010 Census, ~37% of Mississippi’s population is African American and due to the relative youth of the state’s African Americans and the wealth of the state’s whites (who are able to send their kids to private school), most of the state’s public schools are majority black. That percentage would be much higher had not so many African Americans left the state during the Great Migration. The pledge to this flag, which is taught in public schools, reads “I salute the flag of Mississippi and the sovereign state for which it stands with pride in her history and achievements and with confidence in her future under the guidance of Almighty God.” Could you imagine being the descendant of a former slave being made to pledge allegiance to a symbol used by people who fought a war to deny the personhood of your ancestors?
Mississippi’s flag contains the most familiar reference to the Confederacy, but many other state flags have Confederate references. Georgia’s flag contained the Confederate battle flag from 1956 to 2003 and the current flag is modeled after the first national flag of the Confederacy. The flags of Florida and Alabama contain St. Andrew’s Crosses, thought to be references to the stars and bars of Confederate battle flag. The Arkansas state flag contains four stars on a white background, one of which represents the Confederacy, along with a deconstructed stars and bars pattern. North Carolina’s flag is based on a design adopted shortly after the state seceded from the United States. Residents of many states can also get official state license plates with Confederate symbols on them and some state seals have Confederate references.
Lots of progress still to go on that journey towards a post-racial America I guess…
Update: A new Confederate monument was just erected last week near Mobile, Alabama. Here’s what the plaque says about the Confederacy:
The northern Union aggressively prosecuted its war to subjugate the Confederate States. Union forces continued invading and waging war in the field, on cities, and on homesteads in the Confederacy causing more American deaths in both countries than the combined totalitarian regimes of the twentieth century. About two-thirds of these deaths were Union military sent to kill Confederate Americans. The Union’s army was about 3 times larger and it possessed about 20 times the industrial arms capacity of the CSA. It succeeded in militarily prevailing over the Confederate forces after four years. The last major land battle occurred in April of 1865 here and at Ft. Blakeley. The elected government of the CSA was scattered, the American States of that country occupied by northern forces, and the citizens’ rights suppressed.
In April 1865, the Union President was shot watching a comedy play in his capitol of Washington City — almost exactly four years after he sent his warships into the CSA initiating the War Between the States. The Confederacy’s President was seized and imprisoned in May 1865 after he had to flee his capitol of Richmond, Virginia, due to the approach of invading Union forces.
For many, the Civil War never quite ended.




Stay Connected